23/3/ The IPA analysis of canonical signaling pathways showed that some of the IL23responsive proteins were involved in signaling pathways triggered by cytokine receptors and other surface receptors (ie, Granzyme A and IL7 receptor signaling), together with proteins involved in key signaling modules such as p38 MAPK signaling or SAPK/JNK activation (Fig 4B and S4 Table)IL17A is associated with severe asthma and requires IL23 receptor (IL23R) signaling, which is negatively regulated by let7f microRNA Objective We sought to Determine the mechanism by which 17βestradiol (E2) and progesterone (P4) increase IL17A productionHEKBlue™ IL23 cells were generated by stable transfection of HEK293 cells with the human genes for the IL23 receptor and STAT3 to obtain a fully functional IL23 signaling pathway In addition, they express a STAT3inducible secreted embryonic alkaline

Expansion Of Il 23 Receptor Bearing Tnfr2 T Cells Is Associated With Molecular Resistance To Anti Tnf Therapy In Crohn S Disease Gut
Il-23 receptor signaling
Il-23 receptor signaling-7/1/15 IL5 plays important roles in the pathogenesis of asthma, hypereosinophilic syndromes and eosinophildependent inflammatory diseases IL5 is produced by eosinophils, mast cells, Th2 cells, Tc2 cells and gamma delta T cells IL5 exerts influence on different biological activities by associating with the IL5 receptor Associates with IL12RB1 to form the interleukin23 receptor Binds IL23 and mediates Tcells, NK cells and possibly certain macrophage/myeloid cells stimulation probably through activation of the JakStat signaling cascade IL23 functions in innate and adaptive immunity and may participate in acute response to infection in peripheral tissues




Interleukin 23 And Interleukin 17 Importance In Pathogenesis And Therapy Of Psoriasis
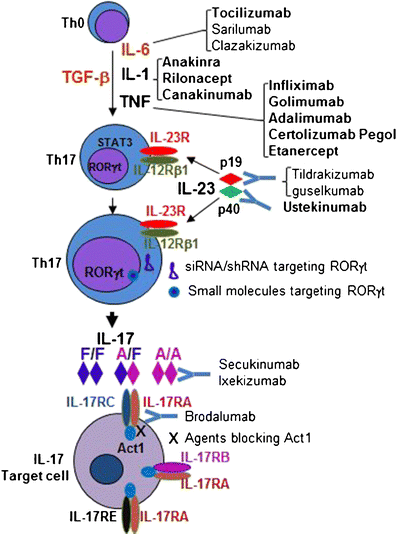
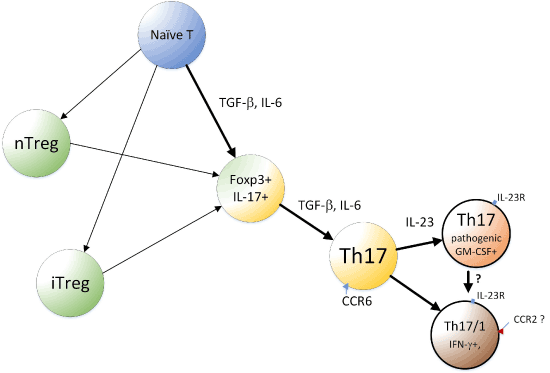
Abstract In the tumor microenvironment, inflammatory cells and molecules influence almost every process; As IL23 regulates the activity of cells of the bone, it is conceivable that in addition to inflammationmediated joint erosion, IL23 may play a role in physiological bone remodeling In this review, we focus on the role of IL23 in autoimmune arthritis in patients and murine models, and provide an overview of IL23 producing and responding cells in autoimmune arthritic jointsIL23 is a heterodimeric member of the IL12 family which shares the p40 subunit but contains a specific p19 subunit which can be recognized by the IL23 receptor (27) Whereas IL6 and IL1 are necessary for induction of Th17 cells, IL23 is responsible for the maintenance of this T helper cell population and production of IL17 (1, 4, 18)
Interleukin23 (IL23) is known to play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of T helper 17 cells It has been previously demonstrated that IL17 is involved in experimental Lyme arthritis, caused by Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria However, the precise role of the IL23 receptor (IL23R) for the B burgdorferiinduced IL17 responses or human Lyme disease has not yetIL12 signaling via IL12 (interleukin 12) receptor is mediated by members of the JakSTAT family Jak2 and either Jak1 or Tyk2 seem to mediate phosphorylation of STAT proteins associated with receptors for cytokines of the IL12 familyThe present invention relates to IL23 receptor antagonists and agonists The use of IL23 receptor antagonists in treating autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, as well as methods of identifying IL23 receptor antagonists and agom'sts
Recombinant Rat IL23 Receptor Protein (Met1Asp367) R02H with a fusion hFc , is expressed in HEK293 Cells With high purity, high biological activity, high stability, and other superior features, you can use this Rat IL23 ReceptorThe present invention relates to novel polypeptides that bind to IL23 receptor and inhibit the binding of IL23 to its corresponding receptor and cell signaling thereof The novel polypeptides of the present invention has a core structure of WX 1 X 2 X 3 W, where W is tryptophan, and X 1 , X 2 and X 3 are amino acids, with the proviso that when one of X 1 , X 2 or X 3 is W, the remaining6/2/ Abstract The IL36 family belongs to a larger IL1 superfamily and consists of three agonists (IL36α/β/γ), one antagonist (IL36Ra), one cognate receptor (IL36R) and one accessory protein (IL1RAcP) The receptor activation follows a twostep mechanism in that the agonist first binds to IL36R and the resulting binary complex recruits IL



Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics




Il23 Receptor Protein Overview Sequence Structure Function And Protein Interaction Sino Biological
13/5/21 The IL23 receptor (IL23R) signaling pathway has pleiotropic effects on the differentiation of osteoclasts and osteoblasts, since it can inhibit or stimulate these processes via different pathwaysBackground/Purpose The interleukin (IL)23/IL17A immune pathway is critical for the development of autoimmune arthritis Systemic exposure of IL23 induced chronic arthritis, increased osteoclast differentiation and systemic bone loss in mice However, the role of IL23 on normal and pathologic bone remodeling is not fully elucidated Here we examined the role of ILTissue expression of IL23R Summary The Human Protein Atlas GENERAL INFORMATIONi General description of the gene and the encoded protein (s) using information from HGNC and Ensembl, as well as predictions made by the Human Protein Atlas project Gene namei



1




The Il 23 Th17 Axis In The Immunopathogenesis Of Psoriasis Sciencedirect
The present invention relates to novel linear and cyclic polypeptides that bind to IL23 receptor and inhibit the binding of IL23 to its corresponding receptor and cell signaling thereof The novel p Clinical 2 Wida Razawy et al DOI /eji Eur J Immunol 18 48 2–229 HIGHLIGHTS REVIEW The role of IL23 receptor signaling in inflammationmediated erosive autoimmune arthritis and bone remodeling Wida Razawy1,2, Marjolein van Driel3 and Erik Lubberts1,2 1 Department of Rheumatology, Erasmus MC, University Medical Center, Rotterdam,13/3/ IL23 plays a role in a signaling pathway that triggers inflammation IL23 inhibitors block the action of IL23, which can help limit the inflammation that causes psoriasis symptoms
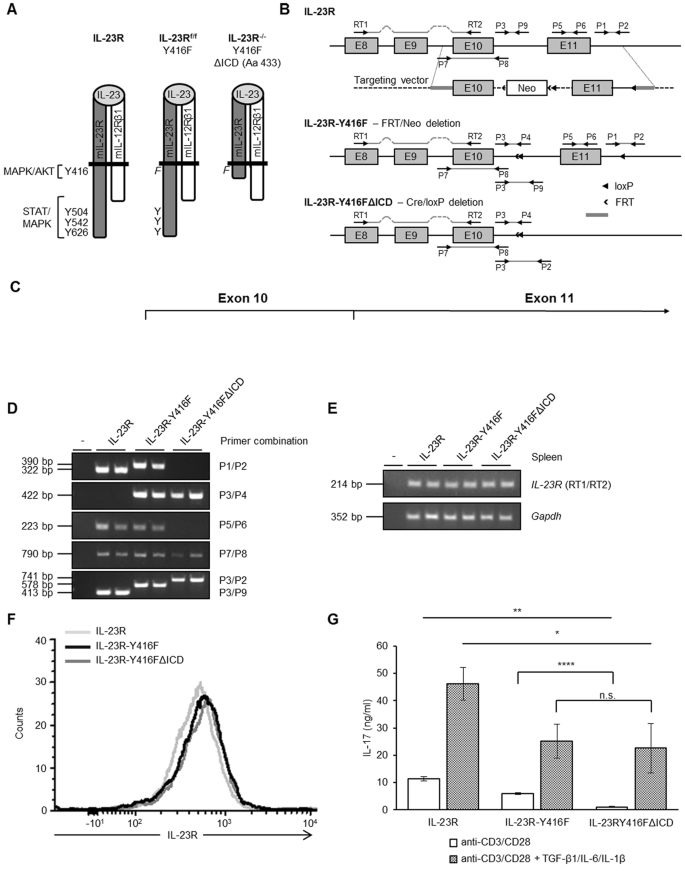



Il 23r Signaling Plays No Role In Myocardial Infarction Scientific Reports
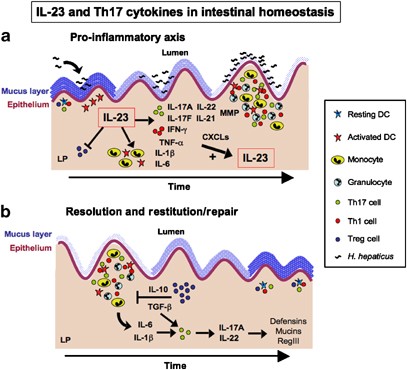



Il 23 And Th17 Cytokines In Intestinal Homeostasis Mucosal Immunology
T H 17 cells are highly plastic (19, 23)Under the influence of IL12, most T H 17 cells that rapidly extinguish retinoic acid receptor–related orphan receptor γt (RORγt) expression upregulate Tbet and a T H 1like program (19, 24, 25)Although IL23 has been shown to be important for T H 17 cell maintenance due to its activation of STAT3, reiterative IL23 signaling also induces T H 17 Estrogen and progesterone decrease let7f microRNA expression and increase IL23/IL23 receptor signaling and IL17A production in patients with severe asthma Dawn C Newcomb, Jacqueline Yvonne Cephus, Madison G Boswell, John M Fahrenholz, Emily W Langley, Amy S Feldman, Weisong Zhou, Daniel E Dulek, Kasia Goleniewska, Kimberly B Woodward,In this study, we investigated the effect of extracellular IL23 in IL23 receptorpositive (IL23R ) esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and explored the mechanisms underlying this effect We analyzed ESCC tumor tissues by immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence staining and found that IL23, which was highly expressed, colocalized with Oct4A in IL23R ESCC cells



2




Interleukin 12 Il 12 And Il 23 Signal Transduction Pathways Il 12 Download Scientific Diagram
It has been previously demonstrated that IL17 is involved in experimental Lyme arthritis, caused by Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria However, the precise role of the IL23 receptor (IL23R) for the B burgdorferiinduced IL17 responses or human Lyme disease has not yet been elucidatedIL23R is a 629 aa, novel subunit of the receptor for cytokine IL23A/IL23 which pairs with the receptor molecule IL12RB1/IL12R beta 1and thus take part in IL23A signaling Signal transduction analysis confirms that this protein associates constitutively with Janus kinase 2 (JAK2), and also binds to transcription activator STAT3 in a liganddependent mannerThe IL23/Th17 axis has been implicated in the development of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) RA and PsA are heterogeneous diseases with substantial burden on patients Increasing evidence suggests that the



1



2
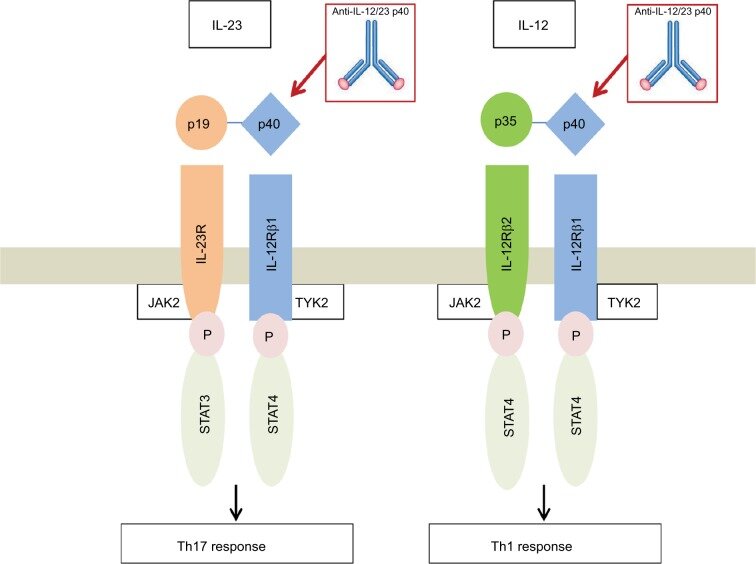
Interleukin23 IL23 is another heterodimeric type I cytokine It is composed of two disulfidelinked polypeptide chains, p19 and IL12 p40 The IL23 receptor also shares the IL12Rβ 1 chain paired to the IL23R The IL23R complex is expressed on T cells and ILCs and regulates production of IL17 (Th17, see below) IL17 is a highly versatile proinflammatory cytokine crucial for a variety of processes, including host defense, tissue repair, the pathogenesis1/8/15 IL23 signaling through the IL23 receptor (IL23R) is important in maintaining and stabilizing the Th17 cell phenotype and increasing IL17A protein expression ( 14 , 15 ) Recently, Let7f, a member of the Let7 microRNA (miRNA) family, negatively regulated IL17A protein expression by decreasing IL23R surface expression on Th17 cells
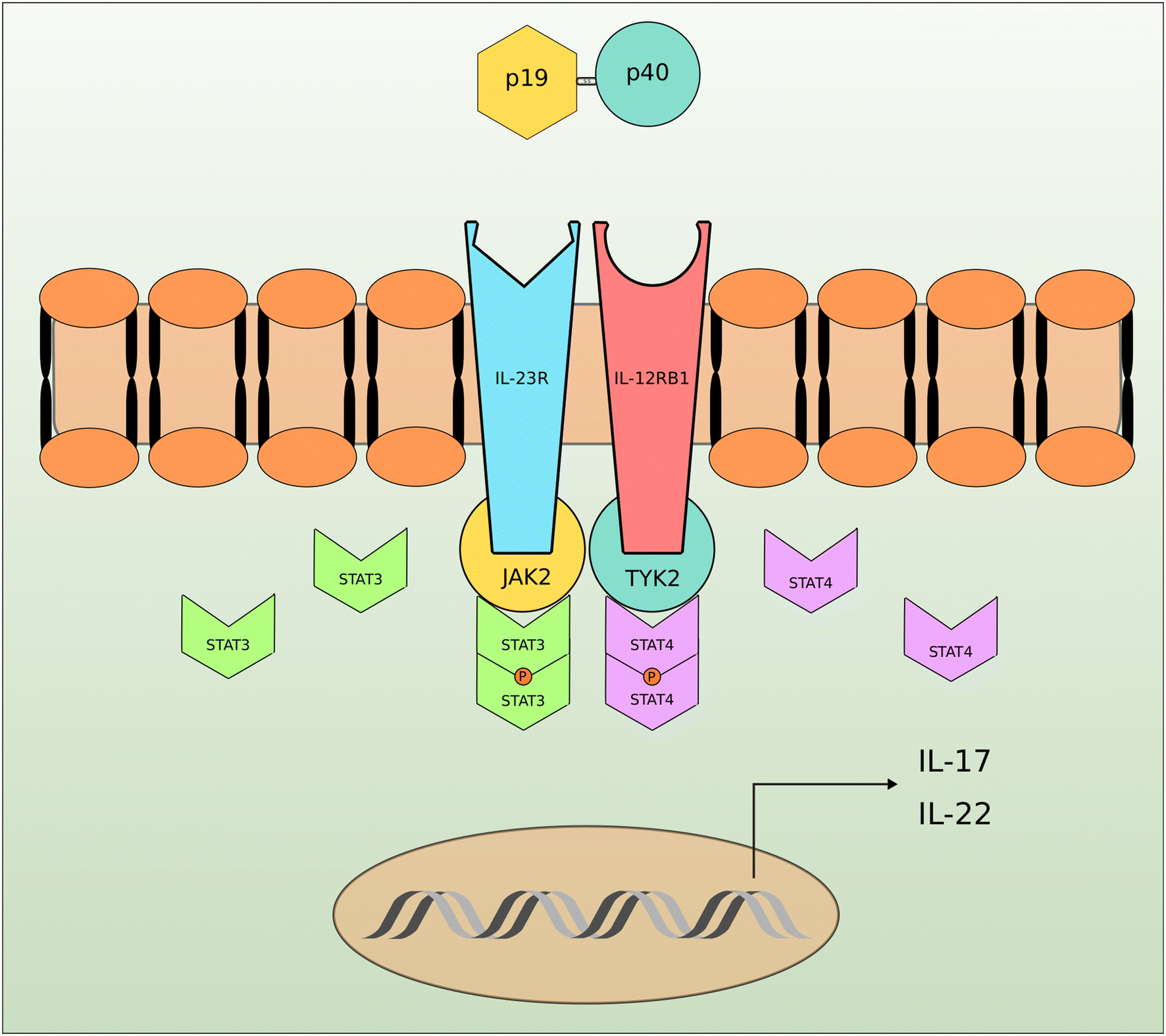



Figure 1 Interleukin 23 And Autoimmune Diseases Current And Possible Future Therapies Springerlink




Il 23 A Master Regulator In Crohn Disease Semantic Scholar
This study demonstrates that IL23R signaling is needed for B burgdorferiinduced IL17 production in vitro and that an IL23R gene SNP leads to impaired IL17 production The results suggest a positive feedback regulation of the IL23 receptor via IL23mediated activation of the JAK/STAT pathwayAssociates with IL12B to form the IL23 interleukin, a heterodimeric cytokine which functions in innate and adaptive immunity IL23 may constitute with IL17 an acute response to infection in peripheral tissues IL23 binds to a heterodimeric receptor complex composed of IL12RB1 and IL23R, activates the JakStat signaling cascade, stimulates memory rather than naive TcellsInterleukin12 (IL12) and IL23 are heterodimeric cytokines that are produced by antigenpresenting cells to regulate the activation and differentiation of lymphocytes, and they share IL12Rβ1 as a receptor signaling subunit



The Dichotomous Pattern Of Il 12r And Il 23r Expression Elucidates The Role Of Il 12 And Il 23 In Inflammation




Cd4 Ccr6 T Cells But Not Gd T Cells Are Important For The Il 23r Dependent Progression Of Antigen Induced Inflammatory Arthritis In Mice Razawy European Journal Of Immunology Wiley Online
Interleukin 23 Receptor (IL23R) Histone 3 (H3) Tumor Protein P53 and both are required for IL23A signaling This protein associates constitutively with Janus kinase 2 IL23 receptor , interleukin 23 receptorlike The IL23/Th17 axis has been implicated in the development of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) RA and PsA are heterogeneous diseases with substantial burden on patients Increasing evidence suggests that the IL23 signaling pathway may be involved Introduction Interleukin23 (IL23), a member of the IL12 cytokine family, is a heterodimeric cytokine, which consists of an IL12p40 subunit, shared with IL12, and an IL23 specific p19 subunit 1The receptor for IL23 consists of IL23Rα in complex with IL12Rβ1, which also serves as a subunit for the IL12 receptor 2Although structurally similar to IL12, IL23 has




A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas
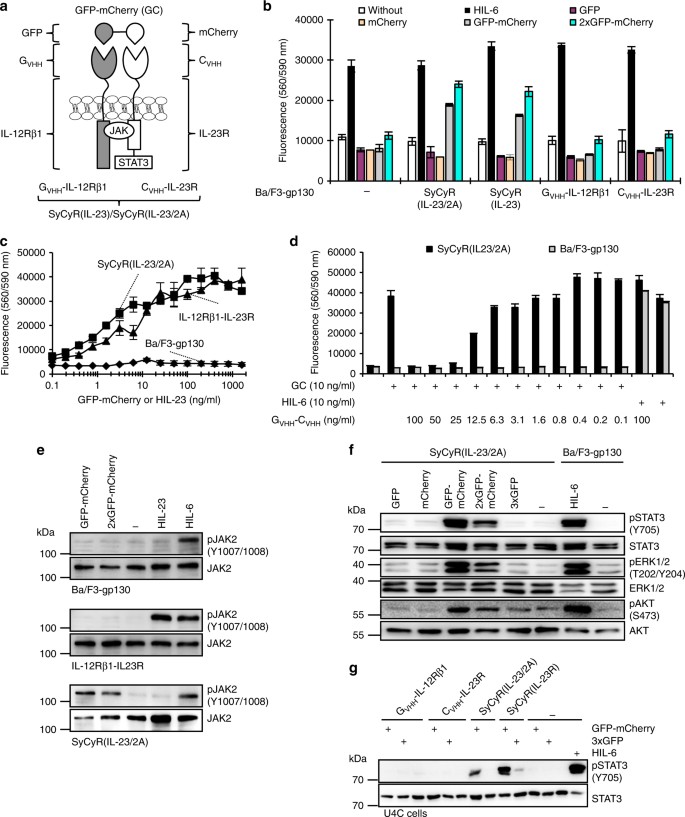



Synthetic Cytokine Receptors Transmit Biological Signals Using Artificial Ligands Nature Communications
Interleukin23 IL23 is another heterodimeric type I cytokine It is composed of two disulfidelinked polypeptide chains, p19 and IL12 p40 The IL23 receptor also shares the IL12Rβ 1 chain paired to the IL23R The IL23R complex is expressed on T cells and ILCs and regulates production of IL17 (Th17, see below)Among them, interleukin23 (IL23) is a proinflammatory molecule that exhibits pro or antitumor properties, but both activities remain poorly understood In this study, we investigated the effect of extracellular IL23 in IL23 receptorpositive (IL23R)23/9/14 Homeostatic IL23 Receptor/IL22 Signaling Controls Intestinal SFB Colonization To assess if homeostatic IL23 expression is required to control the level of SFB colonization in the gut, we quantitated the abundance of bacteria species in Interleukin23 subunit p19 deficient (IL23p19 −/−) or IL23 receptor deficient (IL23R −/−) mice vs WT littermates by quantitative PCR




Interleukin 23 A New Atherosclerosis Target Journal Of Interferon Cytokine Research



Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities Document Gale Academic Onefile
IL23 signaling pathway IL23 plays important role in expanding and maintaining the Th17 cell population, a novel Tcell subset involved in antimicrobial immune response and establishment of many autoimmune diseases 1 IL23 receptor is composed of IL12RB1 and IL23R IL23R associates with JAK2 and in a liganddependent manner with STAT3 2Due to similarities in the subunit composition of the IL12 family cytokines, many of the receptors for these cytokines also have common chains and activate seemingly comparable downstream signaling pathways IL12 and IL23 both signal through heterodimeric receptor complexes that contain IL12 R beta 1 paired with either IL12 R beta 2 for Specific targeting of the IL23 receptor, using a novel small peptide noncompetitive antagonist, decreases the inflammatory response Christiane Quiniou,1 Maria DomínguezPunaro,2 Frank Cloutier,1 Atefeh Erfani,1 Jamila Ennaciri,1 Durgajini Sivanesan,5 Mélanie Sanchez,4 Gaëlle Chognard,2,3 Xin Hou,1 José Carlos Rivera,2 Claudine Beauchamp,6 Guy Charron,6 Marie




Inflammatory Disease Protective R381q Il23 Receptor Polymorphism Results In Decreased Primary Cd4 And Cd8 Human T Cell Functional Responses Pnas




Il 23 Il 23r Signaling Induces Rort And Il 17 A Flow Cytometry Of Download Scientific Diagram
7/1/15 Protein 1 Regulation of gene expression Receptor IL3 Signaling Pathway Enzyme complex mRNA Protein Ligand MAPK8 IL3RA ENPP3 TGFB1 CD69 VAV1 MAPK1 IL8 FOS CD86 BCL2 CCR3 HCK SYK FYN IL5RA LYN TEC1 P P P P P P P P YWHAB GRB2 PRKACA P INPP5D IL3RA BAD P PIK3R2 STAT5B BCL2L1 P SOS1 CSF2RB STAT5A MAP2K1 P YWHAQ P SRC P AKT1 PTPN6 PHomeostatic IL23 receptor signaling limits Th17 response through IL22–mediated containment of commensal microbiota Vincent FengSheng Shiha, Jennifer Coxa,1, Noelyn M Kljavinb, Hart S Denglera, Mike Reicheltc, Pawan Kumard, Linda Rangellc, Jay K Kollsd, Lauri Diehlc, Wenjun Ouyanga, and Nico Ghilardia,2 Departments of aImmunology, bMolecular Biology, andThe present invention relates to novel polypeptides that bind to IL23 receptor and inhibit the binding of IL23 to its corresponding receptor and cell signaling thereof The novel polypeptides of the present invention has a core structure of WX1X2X3W, where W is tryptophan, and X1, X2 and X3 are amino acids, with the proviso that when one of X1, X2 or X3 is W, the remaining two of X1,
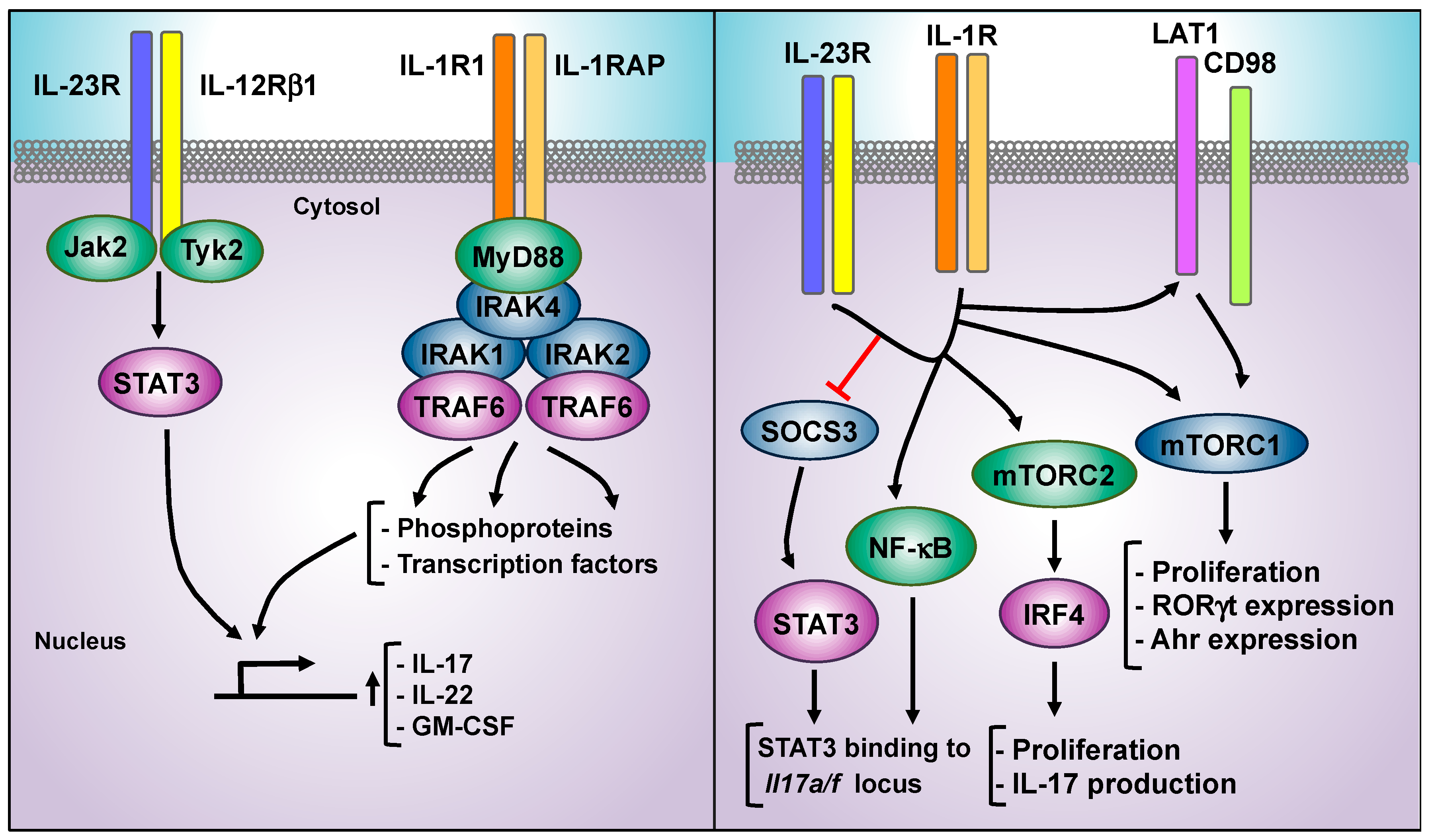



Cells Free Full Text Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities




Profile Of Interleukin 22 In Gut Mucosal Health And Disease Ijicmr
IL4 Signaling Pathways Click on the "Effects" button below to reveal the primary biological effects of IL4 signaling in different immune cell types Click on one of the other cytokines below for information on a different common cytokine receptor gammachain family member15/1/18 The receptor for IL‐23 consists of IL‐23Rα in complex with IL‐12Rβ1, which also serves as a subunit for the IL‐12 receptor 2 Although structurally similar to IL‐12, IL‐23 has the unique ability of amplifying and stabilizing the proliferation of IL‐17 secreting T




Interleukin 23 Receptor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
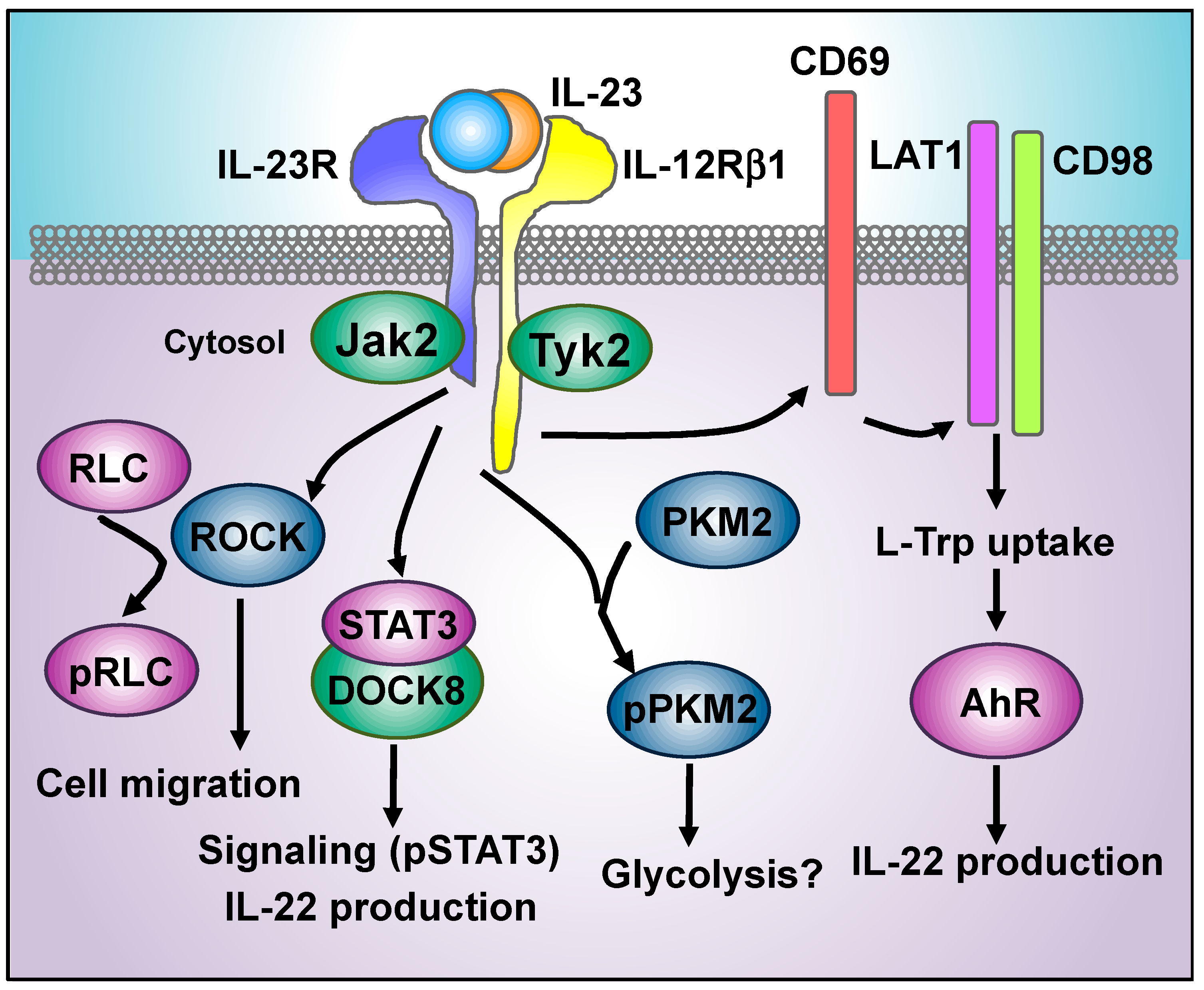



Cells Free Full Text Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities




Interleukin 23 Wikipedia




Stelara Ustekinumab For The Treatment Of Moderate To Severe Crohn S Disease Clinical Trials Arena
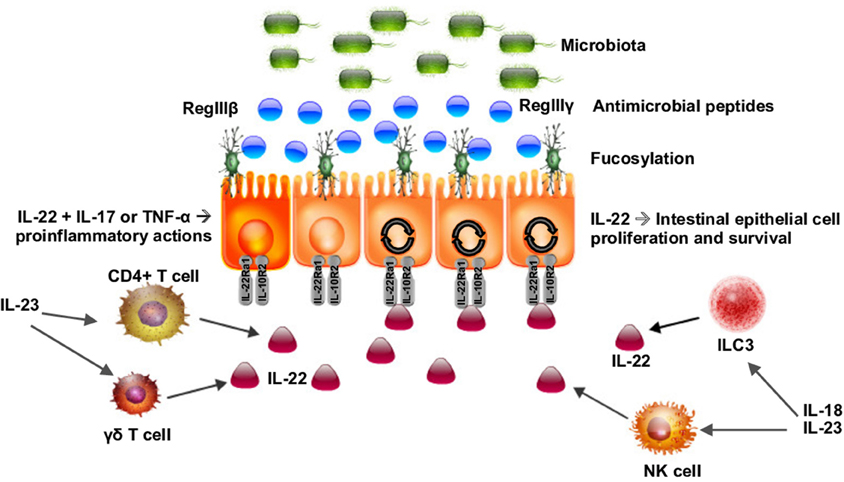



Frontiers Interleukin 22 Signaling In The Regulation Of Intestinal Health And Disease Cell And Developmental Biology
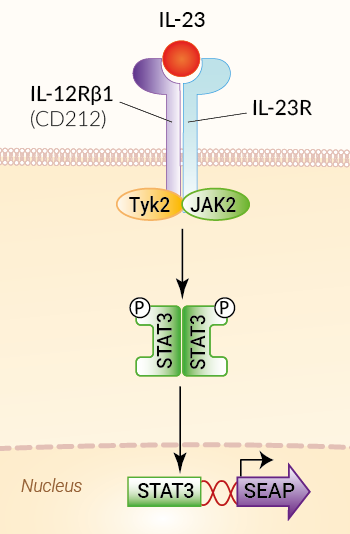



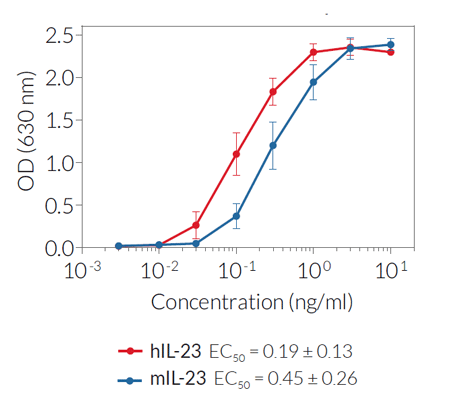
Hek Blue Il 23 Cells Il 23 Reporter Cells Invivogen




The Il 23 Axis Genes Associationed With Psoriasis Il 12 And Il 23 Share Download Scientific Diagram




Il 23 In Inflammatory Bowel Diseases And Colon Cancer Sciencedirect




Discovery Of The Il 23 Il 17 Signaling Pathway And The Treatment Of Psoriasis The Journal Of Immunology




Il 12 Family Signaling Pathway Sino Biological



Schematic Representation Of Il 12 And Il 23 With Their Receptors And Download Scientific Diagram




Therapeutics Targeting The Il 23 And Il 17 Pathway In Psoriasis The Lancet




Expansion Of Il 23 Receptor Bearing Tnfr2 T Cells Is Associated With Molecular Resistance To Anti Tnf Therapy In Crohn S Disease Gut




Stat3 And Nf Kb Signal Pathway Is Required For Il 23 Mediated Il 17 Production In Spontaneous Arthritis Animal Model Il 1 Receptor Antagonist Deficient Mice The Journal Of Immunology



Hek Blue Il 23 Cells Il 23 Reporter Cells Invivogen




Il 12 Family Cytokines Receptors And Signaling Pathways Il 12 Download Scientific Diagram




Figure 2 Skewed Helper T Cell Responses To Il 12 Family Cytokines Produced By Antigen Presenting Cells And The Genetic Background In Behcet S Disease




Il 23 Signaling Pathway Il 23 Is A Heterodimeric Cytokine Composed Of Download Scientific Diagram




Il 23 Producing Il 10ra Deficient Gut Macrophages Elicit An Il 22 Driven Proinflammatory Epithelial Cell Response




Rbpj Controls Development Of Pathogenic Th17 Cells By Regulating Il 23 Receptor Expression Sciencedirect




Psoriatic Skin Inflammation Is Promoted By C Jun Ap 1 Dependent Ccl2 And Il 23 Expression In Dendritic Cells Embo Molecular Medicine



How Can We Manipulate The Il 23 Il 17 Axis Springerlink



Plos Biology Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics



Factors Regulating Th17 Cells A Review




A Balance Of Interleukin 12 And 23 In Cancer Trends In Immunology




Synthetic Deletion Of The Interleukin 23 Receptor Il 23r Stalk Region Led To Autonomous Il 23r Homodimerization And Activation Molecular And Cellular Biology
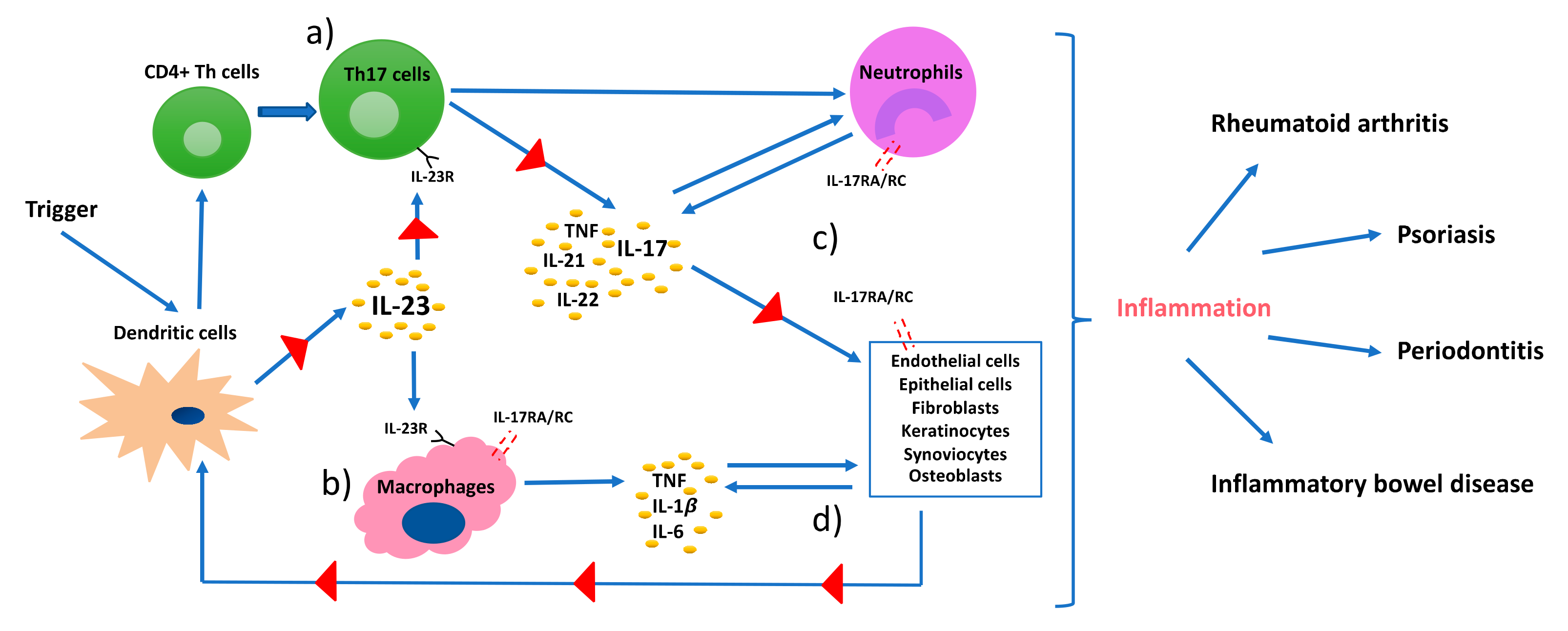



Ijms Free Full Text Th17 Cells And The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In The Pathogenesis Of Periodontitis And Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Html




Synthetic Deletion Of The Interleukin 23 Receptor Il 23r Stalk Region Led To Autonomous Il 23r Homodimerization And Activation Molecular And Cellular Biology



1
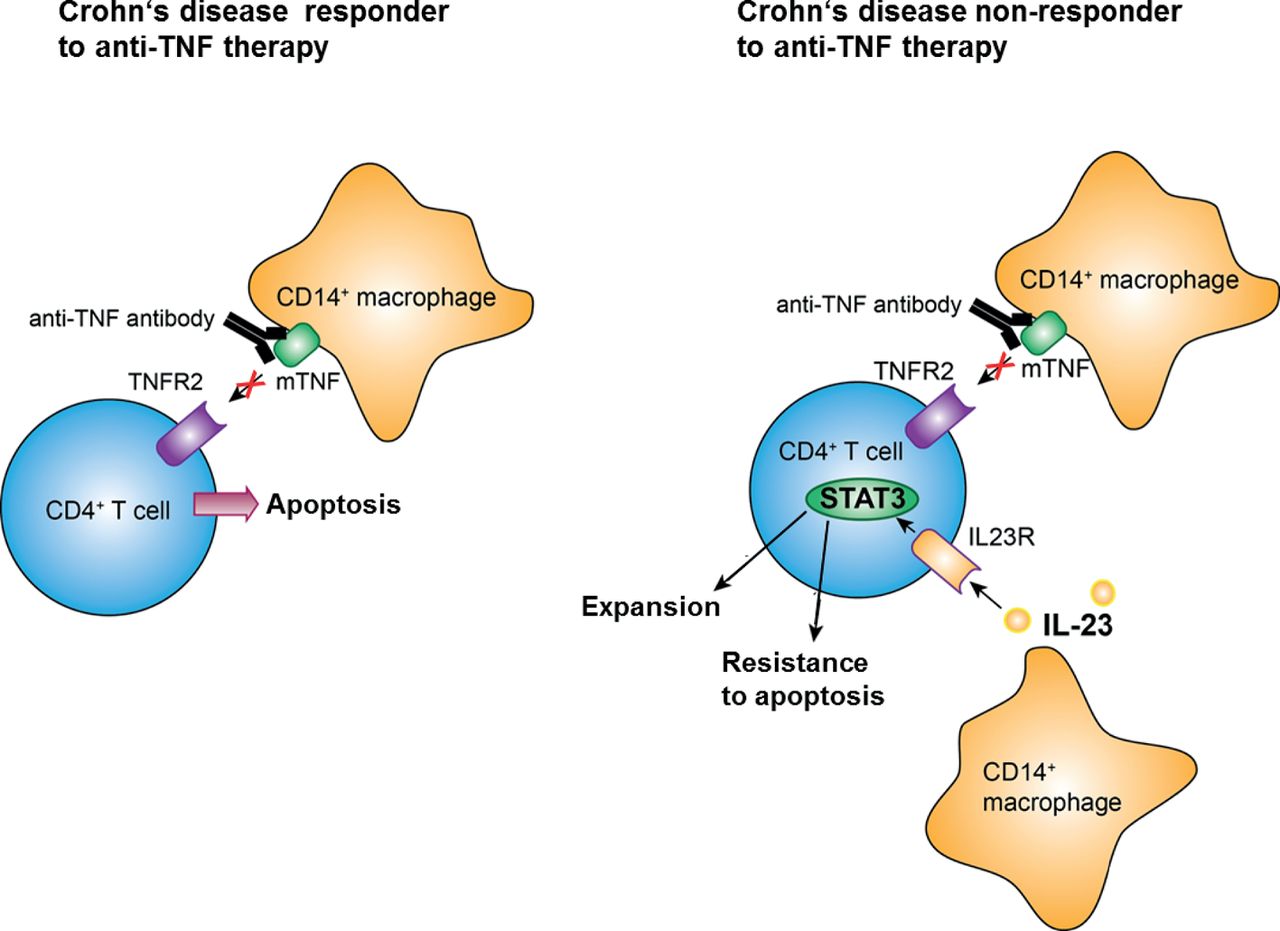



Expansion Of Il 23 Receptor Bearing Tnfr2 T Cells Is Associated With Molecular Resistance To Anti Tnf Therapy In Crohn S Disease Gut




Interleukin 23 And Interleukin 17 Importance In Pathogenesis And Therapy Of Psoriasis




Interleukin 23 Promotes A Distinct Cd4 T Cell Activation State Characterized By The Production Of Interleukin 17 Journal Of Biological Chemistry



1
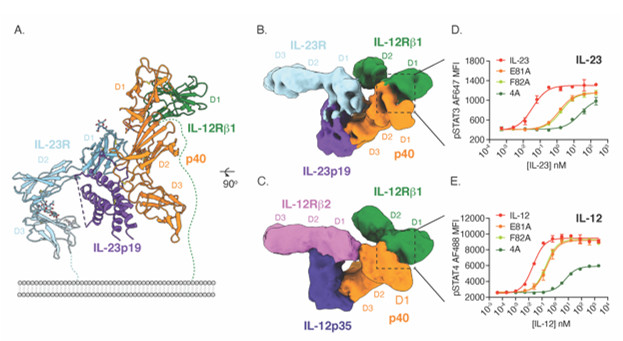



Structure Based Tuning Of Interleukin Receptor Complexes To Promote Anti Tumor Immunity Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource




Overview Of Jak Binding Sites Within The Il 23 Receptor Complex Download Scientific Diagram




The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriatic Arthritis Sciencedirect
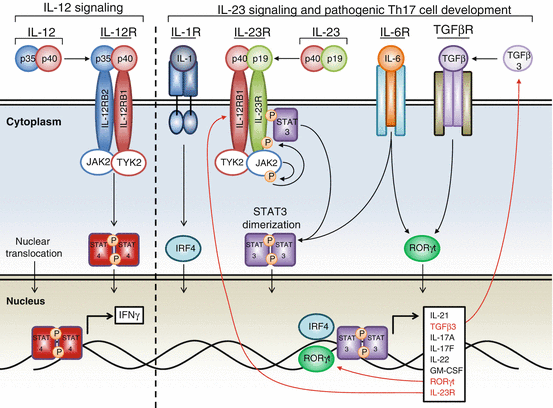



Il 23 In Health And Disease Springerlink




A Receptor For The Heterodimeric Cytokine Il 23 Is Composed Of Il 12rb1 And A Novel Cytokine Receptor Subunit Il 23r The Journal Of Immunology
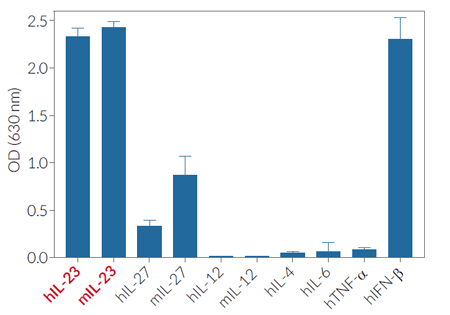



Hek Blue Il 23 Cells Il 23 Reporter Cells Invivogen




Vitamin D Downregulates The Il 23 Receptor Pathway In Human Mucosal Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology
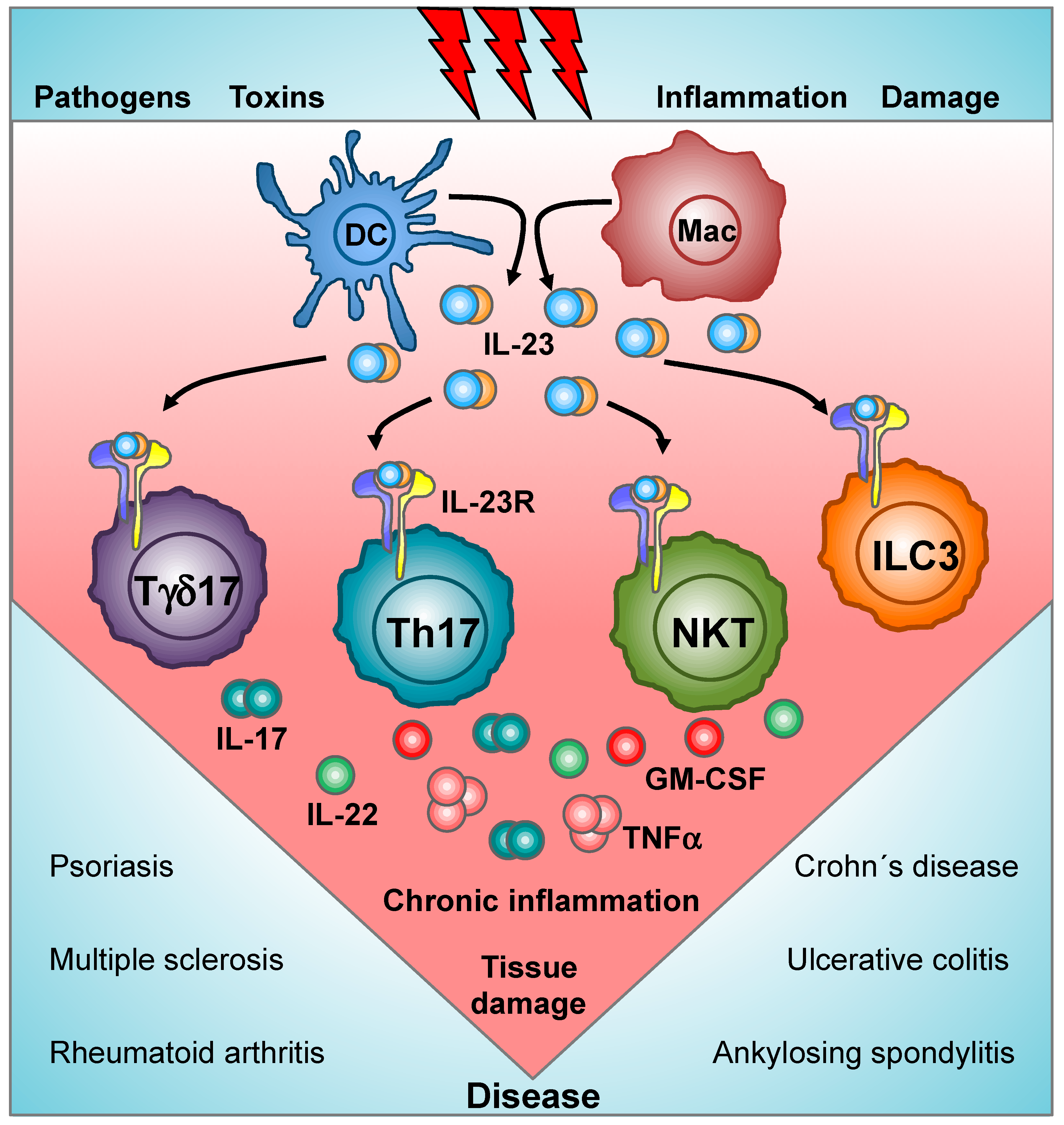



Cells Free Full Text Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities




Homeostatic Il 23 Receptor Signaling Limits Th17 Response Through Il 22 Mediated Containment Of Commensal Microbiota Pnas
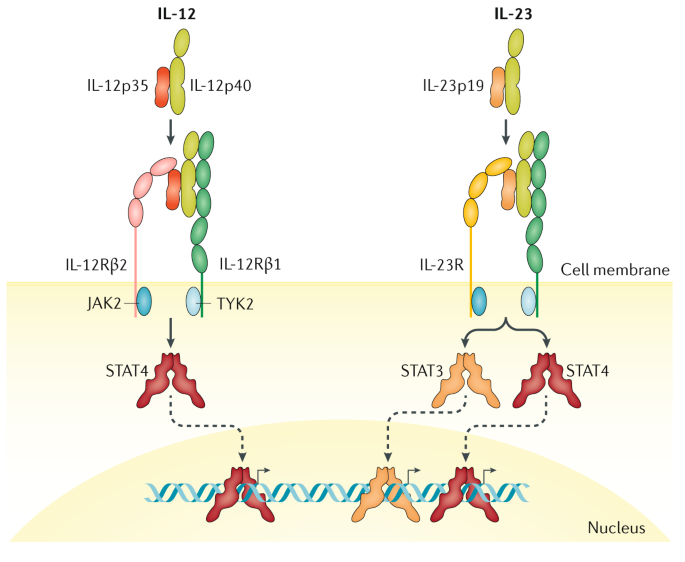



Il 12 Il 23 And Il 17 In Ibd Immunobiology And Therapeutic Targeting Nature Reviews Gastroenterology Hepatology




A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas
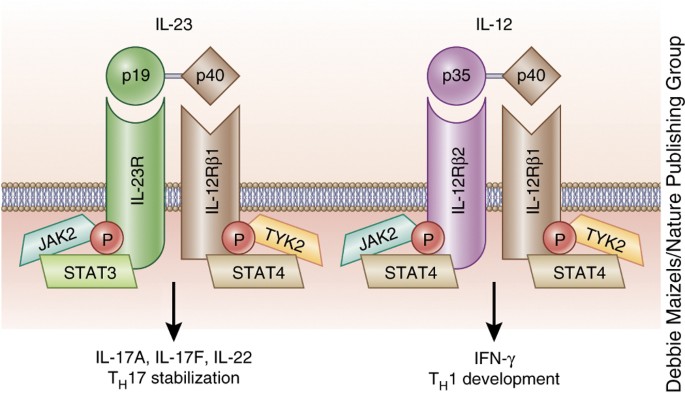



Il 12 And Il 23 Cytokines From Discovery To Targeted Therapies For Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Nature Medicine




A Receptor For The Heterodimeric Cytokine Il 23 Is Composed Of Il 12rb1 And A Novel Cytokine Receptor Subunit Il 23r The Journal Of Immunology




Il 17 Signaling Pathway Creative Diagnostics




Interleukin 23 Subunit Alpha Wikipedia




Morphine Inhibits Murine Dendritic Cell Il 23 Production By Modulating Toll Like Receptor 2 And Nod2 Signaling Journal Of Biological Chemistry



Frontiers The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 Axis Links Adaptive And Innate Immunity In Psoriasis Immunology




Regulation Of The Il 23 And Il 12 Balance By Stat3 Signaling In The Tumor Microenvironment Abstract Europe Pmc



Frontiers The Il 17 Family Of Cytokines In Psoriasis Il 17a And Beyond Immunology



The Il 23 Il 17 Pathway In Human Chronic Inflammatory Diseases New Insight From Genetics And Targeted Therapies Genes Immunity



Cells Free Full Text Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities




Jci Insight Il 23r Activated Stat3 Stat4 Is Essential For Th1 Th17 Mediated Cns Autoimmunity




A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas
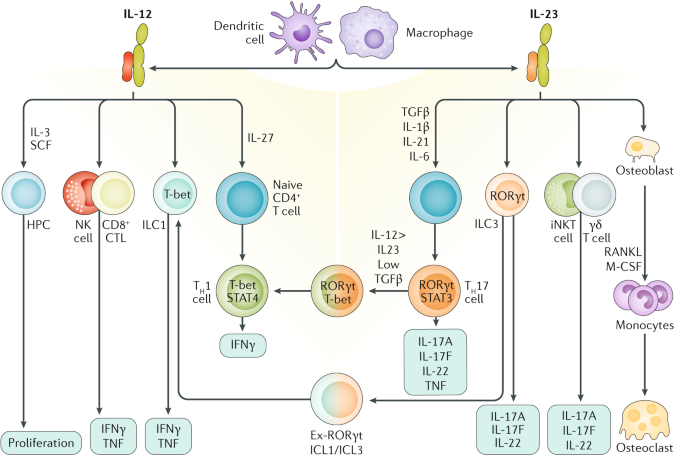



Il 12 Il 23 And Il 17 In Ibd Immunobiology And Therapeutic Targeting Nature Reviews Gastroenterology Hepatology




Pathophysiology And Inhibition Of Il 23 Signaling In Psoriatic Arthritis A Molecular Insight Sciencedirect




Il 23 And Il 1b Drive Human Th17 Cell Differentiation And Metabolic Reprogramming In Absence Of Cd28 Costimulation Cell Reports




Therapeutics Targeting The Il 23 And Il 17 Pathway In Psoriasis The Lancet



2




Pdf Decoding Il 23 Signaling Cascade For New Therapeutic Opportunities Semantic Scholar




Estrogen And Progesterone Decrease Let 7f Microrna Expression And Increase Il 23 Il 23 Receptor Signaling And Il 17a Production In Patients With Severe Asthma Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology
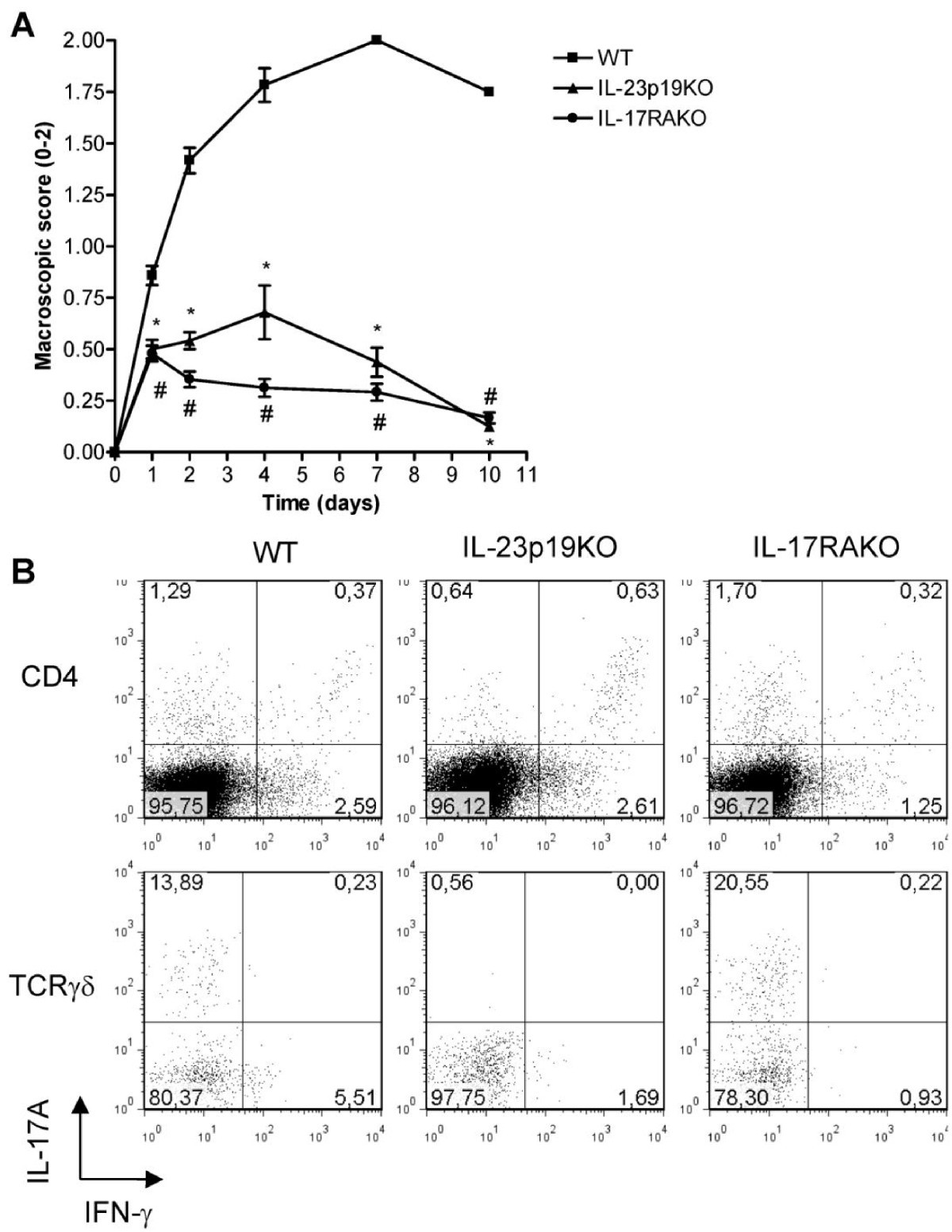



Interleukin 23 Is Critical For Full Blown Expression Of A Non Autoimmune Destructive Arthritis And Regulates Interleukin 17a And Rorgt In Gd T Cells Arthritis Research Therapy Full Text
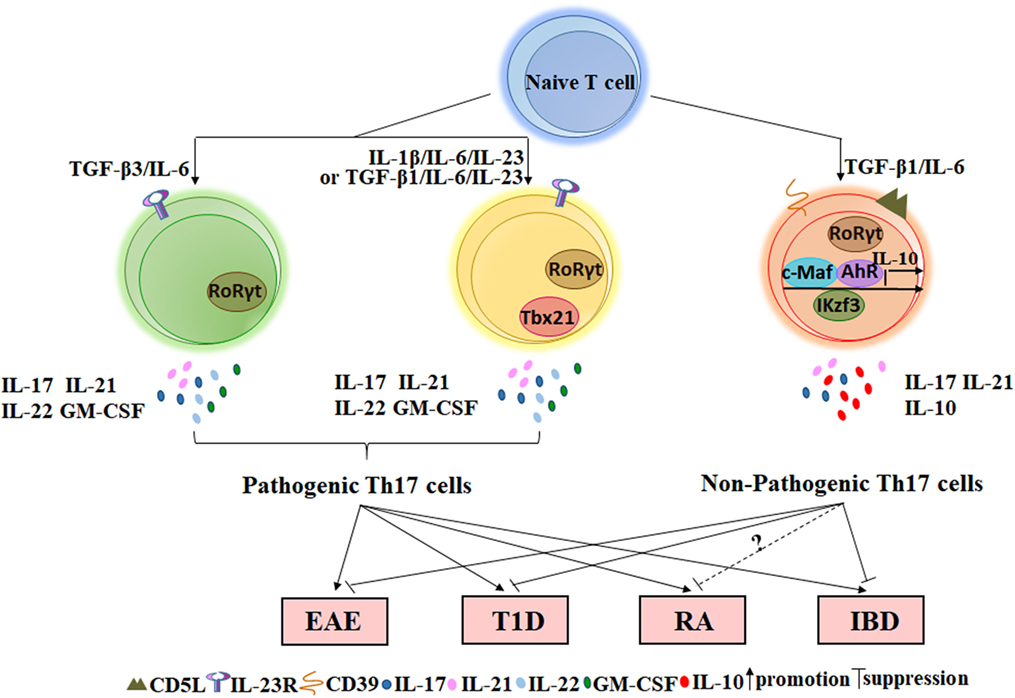



Frontiers Insight Into Non Pathogenic Th17 Cells In Autoimmune Diseases Immunology




Pathways Jak Stat Signaling Www Antibodies Online Com



2




Discovery Of The Il 23 Il 17 Signaling Pathway And The Treatment Of Psoriasis The Journal Of Immunology




Signaling By Il 12 And Il 23 And The Immunoregulatory Roles Of Stat4 Watford 04 Immunological Reviews Wiley Online Library
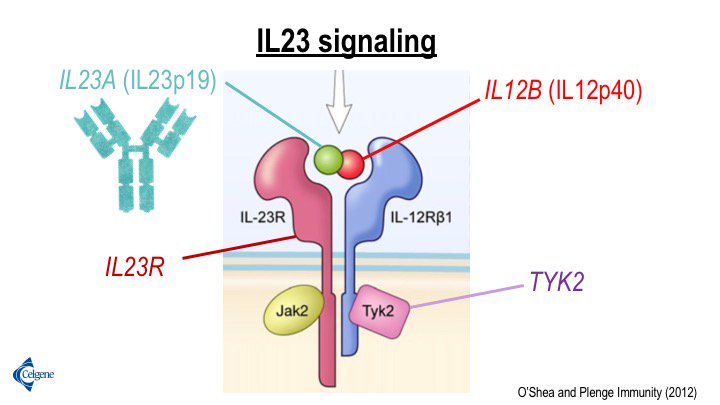



Robert Plenge בטוויטר The Il23 Signaling Pathway In Psoriasis Has Particular Strong Genetic Support Both Subunits Of The Il23 Ligand One Subunit Of The Il23 Receptor And Multiple Intracellular Signaling Molecules T Co Kinawgh01t




Supplemental Materials For T Cell Intrinsic Prostaglandin E2 Ep2 Ep4 Signaling Is Critical In Pathogenic Th17 Cell Driven Inflammation Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology
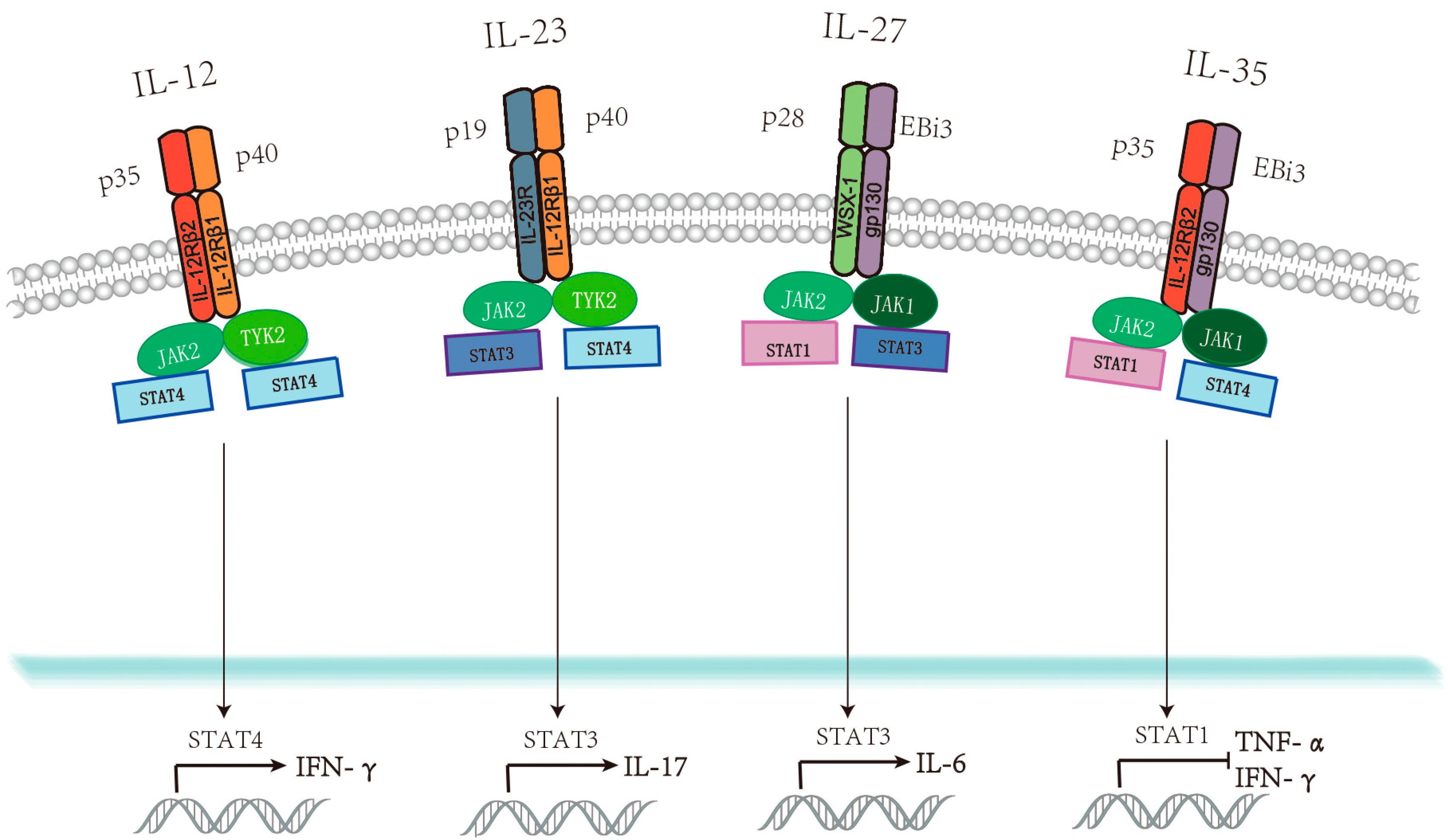



Viruses Free Full Text Immunoregulatory Functions Of The Il 12 Family Of Cytokines In Antiviral Systems Html
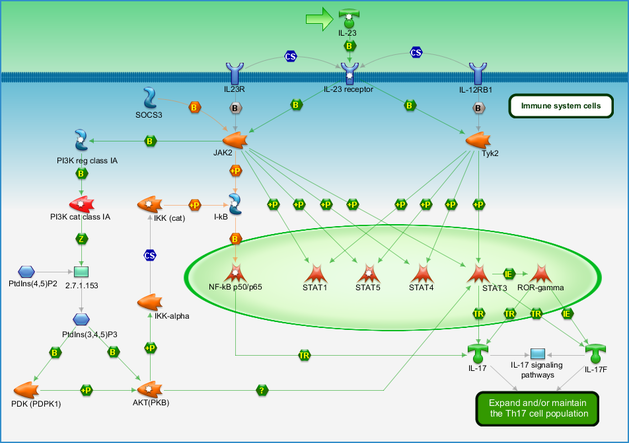



Immune Response Il 23 Signaling Pathway Pathway Map Primepcr Life Science Bio Rad




Microenvironmental Regulation Of The Il 23r Il 23 Axis Overrides Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Indolence




Epithelial Il 23r Signaling Licenses Protective Il 22 Responses In Intestinal Inflammation Topic Of Research Paper In Biological Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




Epithelial Il 23r Signaling Licenses Protective Il 22 Responses In Intestinal Inflammation Sciencedirect
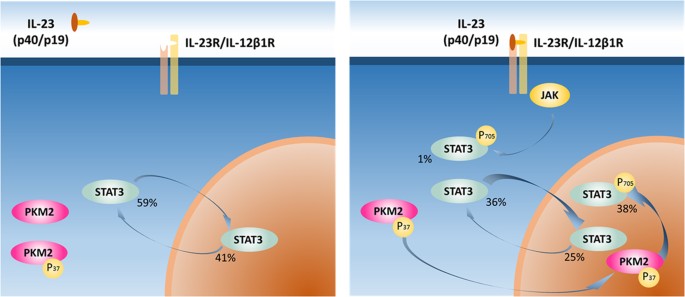



Integrative Phosphoproteomics Links Il 23r Signaling With Metabolic Adaptation In Lymphocytes Scientific Reports
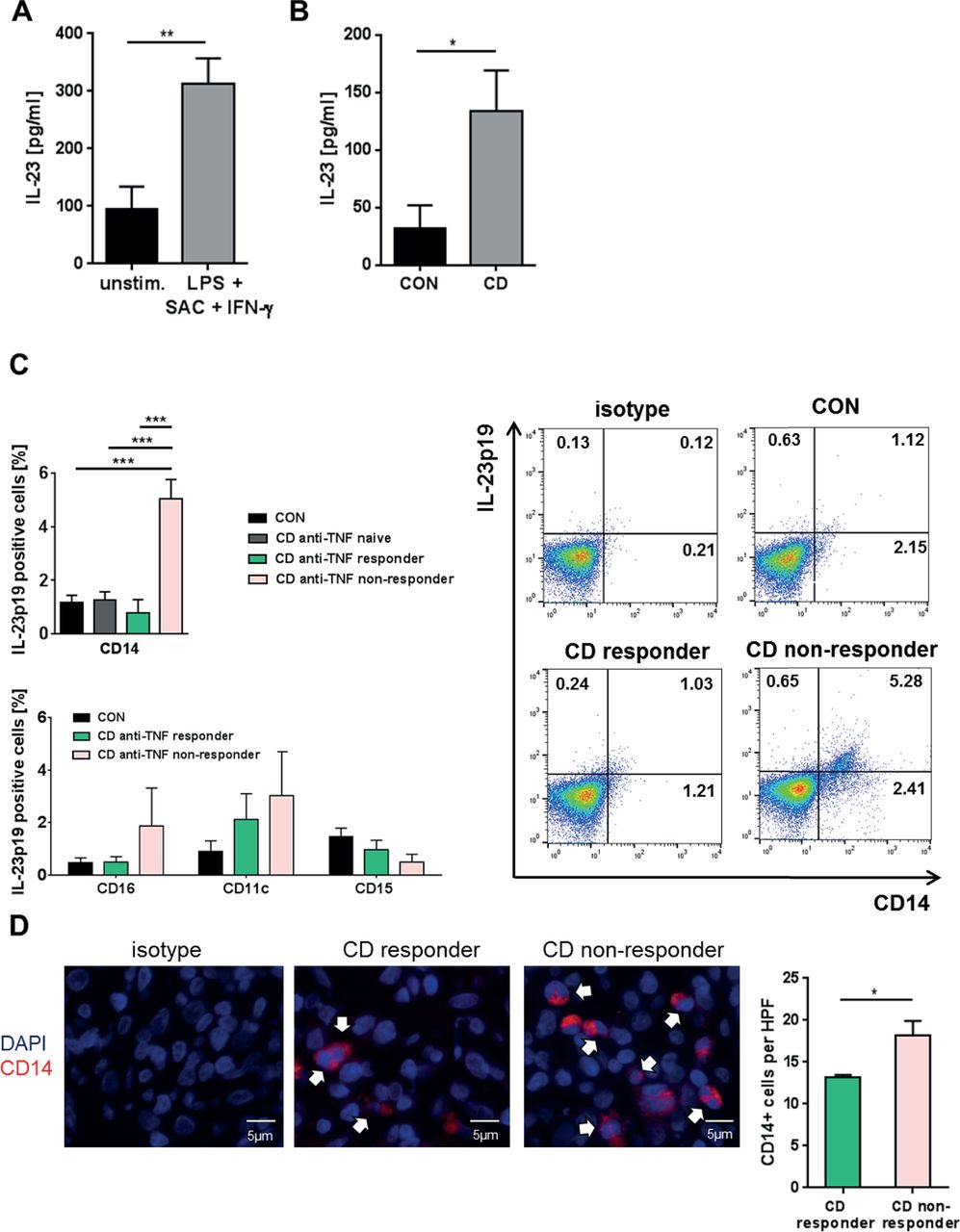



Expansion Of Il 23 Receptor Bearing Tnfr2 T Cells Is Associated With Molecular Resistance To Anti Tnf Therapy In Crohn S Disease Gut




Il 23 A Cytokine That Acts On Memory T Cells




Il 12 Family Signaling Pathways R D Systems




Ustekinumab And Anti Interleukin 23 Agents In Crohn S Disease Gastroenterology Clinics




Jci Tissue Specific Therapy In Immune Mediated Kidney Diseases New Arguments For Targeting The Il 23 Il 17 Axis



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿